Carbon Market

Specialized Areas
Forest Carbon Program
On its surface, carbon markets are trading platforms in which carbon credits are sold and bought. One carbon credit equals one tonne of carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2eq) of GHG reduced or removed. Underneath it, there are climate action projects, decarbonization efforts, offsetting, science-based measurement, reporting and verification, multi-stakeholder engagement and partnerships etc.
We, at the OLOLT Center, like to emphasize the carbon market as an efficient, transparent, and equitable platform that elevates multi-stakeholder collaboration on climate change. Global benchmarks for high-integrity carbon credits are established by the The Integrity Council for the Voluntary Carbon Market (ICVCM) as the Core Carbon Principles (CCPs). These principles of carbon markets ensure equal opportunities and benefits for diverse interest groups including communities.
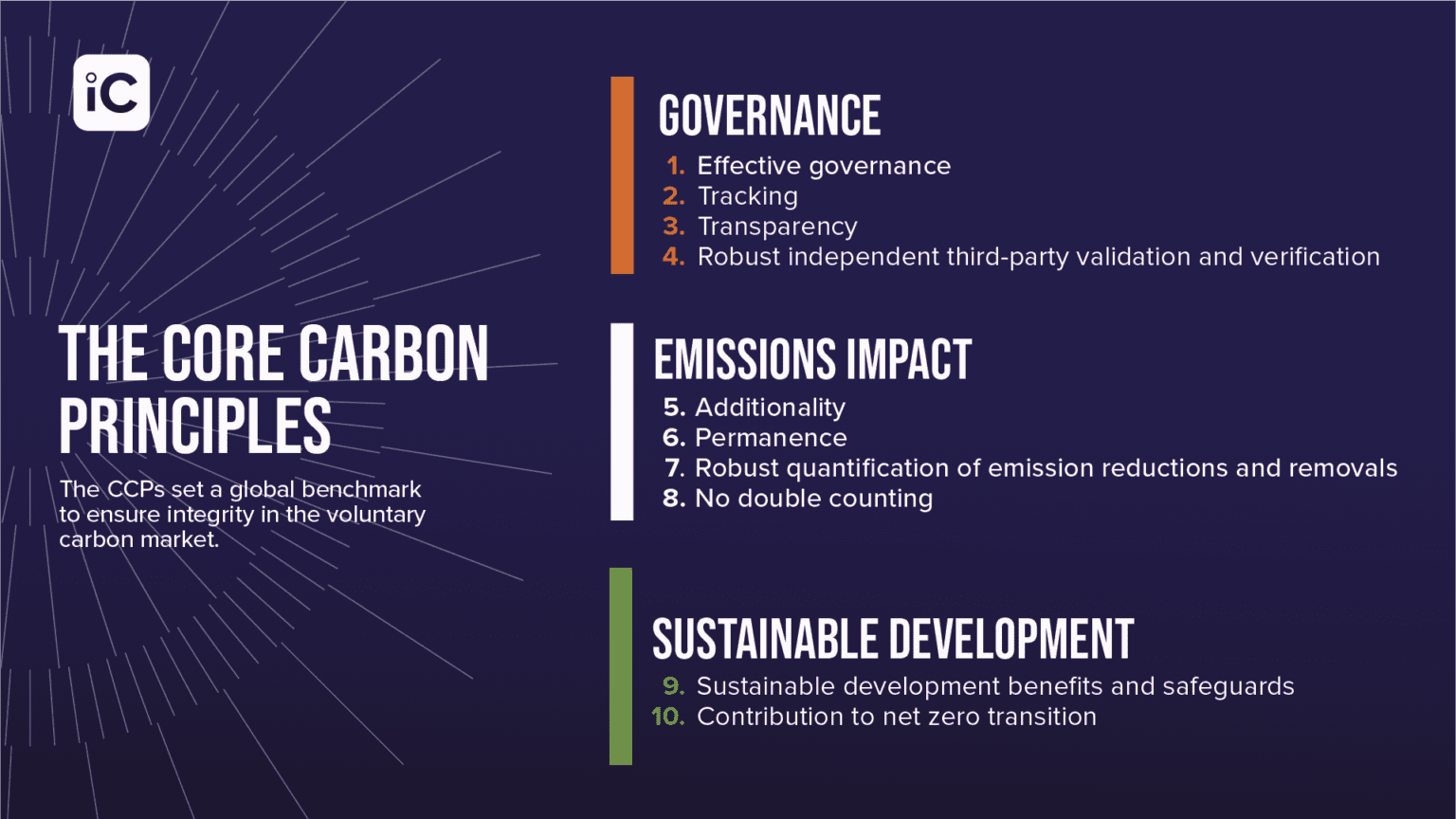
Source: The 10 Core Carbon Principles, The Integrity Council for the Voluntary Carbon Market, 2023
Overall process of carbon markets
GHG reduction or removal projects must follow a robust set of criteria, requirements, and science-based emissions calculation methodologies to pass the third-party validation and verification for generating high quality carbon credits.
Frequently Asked Questions
Forest Carbon Program
Mongolian Forest Carbon Program (MFCP) is a voluntary and national carbon market standard for afforestation, reforestation and agroforestry projects in Mongolia.
MFCP is supported by the US Embassy in Mongolia, and designed in collaboration with the Hamerkop Climate Impact ltd.
Aligned with the international carbon principles, supported by the science-based methodology, independent validation and verification, and transparent registry where forest carbon credits are tracked - MFCP enables individuals, companies, or organizations to reduce, offset GHG emissions, and contribute towards the Billion Tree Campaign and Nationally Determined Contributions of Mongolia.
Applicability:
- Afforestation, reforestation, and agroforestry projects
Methodology:
- MFCS accepted methodologies - Methodology for Afforestation, Reforestation, Agroforestry (ARA) GHG emission reduction and sequestration in Mongolia (V.01)
Crediting period: 30-60 years
MFCP Principles
Project Eligibility Criteria
Other related questions
For more information reach out to contact@cccmdc.mn.
Agriculture Carbon Program
Mongolia's agriculture sector plays a vital role in its traditional culture, lifestyle, and economy. As of 2022, it contributes approximately 13% to the GDP and employs 26% of the population.[1] Herders, who account for 10% of the total population, are central to this sector, caring for over 71 million livestock[2] across 112 thousand hectares of pastureland.[3]
[1] The Gross Domestic Product by Sectors, National Statistics Office, 2022
[2] Statistics on Livestock, National Statistics Office, 2022
[3] Pasture Use Update, Ministry of Food, Agriculture and Light Industry, 2023
Despite its importance to the economy, the sector faces considerable vulnerability to climate change, exacerbated by the increasing frequency and intensity of climate-related hazards.
The intertwining relationship between climate change and agriculture in Mongolia is complex. On one hand, agriculture contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, while on the other, it is profoundly affected by climate change.
Mongolia's National Greenhouse Gas Inventory reveals that the agriculture sector is the largest emitter (51.97% of the national total GHG emission), generating 22.4 million tCO2e[4] due to the increased number of livestock. Pasture-based livestock and rain-fed agriculture practices are highly exposed and vulnerable to climate-induced disasters.
[4] National GHG Inventory, Climate Change Research and Cooperation Center, 2023
Acknowledging the significance of mitigating emissions in the agriculture sector and strengthening its resilience to climate change, the OLOLT Center is exploring market-based schemes to be introduced in the sector. Our aim is to create an enabling environment for an innovative and inclusive financing mechanism for a just transition in the agriculture sector.


